
Diet and Pranayama – Milk and Ghee is recommended
Diet and Pranayama – Milk and Ghee is recommended. At the beginning period of pranayama practice, food, consisting of milk and ghee is recommended very
Karuna Yoga Vidya Peetham Bangalore


Diet and Pranayama – Milk and Ghee is recommended. At the beginning period of pranayama practice, food, consisting of milk and ghee is recommended very

Veerasana (Hero’s Pose) Ekam padam tathaikasmin vinyased uruni sthiram / Itarasmims tatha chorum virasanam itiritam//(Chapter -1, Verse 21). Placing one foot by the opposite thigh
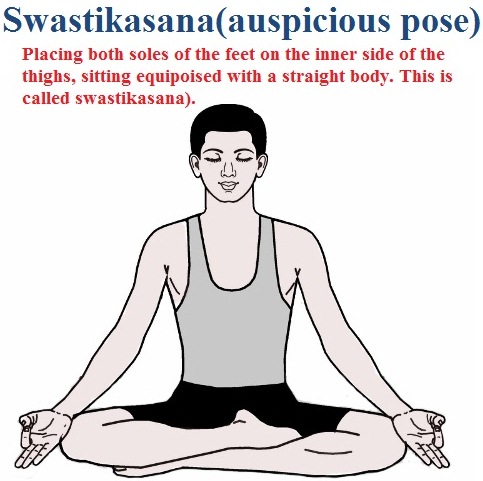
Swastikasana (auspicious pose) Janurvor antare samyak krtva padatale ubhe / Rjukayah samasinah svastikam tat prachakshate//(Chapter -1, Verse 19). Placing both soles of the feet on

Simhasana (lion’s pose) Ghulphau cha vrshanasyadhah Sivantyah parsvayoh kshipet/ Dakshine savyaghulpham tu Dakshaghulpham tu savyake//(Chapter -1, Verse-50). Place the ankles below the scrotum, right ankle

Siddhasana (Adept’s Pose) Yonisthanakam angghrimulaghatitam Krtva drdham vinyaset / Mendhre padam athaikameva hrdaye Krtva hanum susthiram // Sthanuh samyamitendriyoa chaladrsa pasyed bhruvor antaram/ Hyetan mokshakapatabhedajanakam
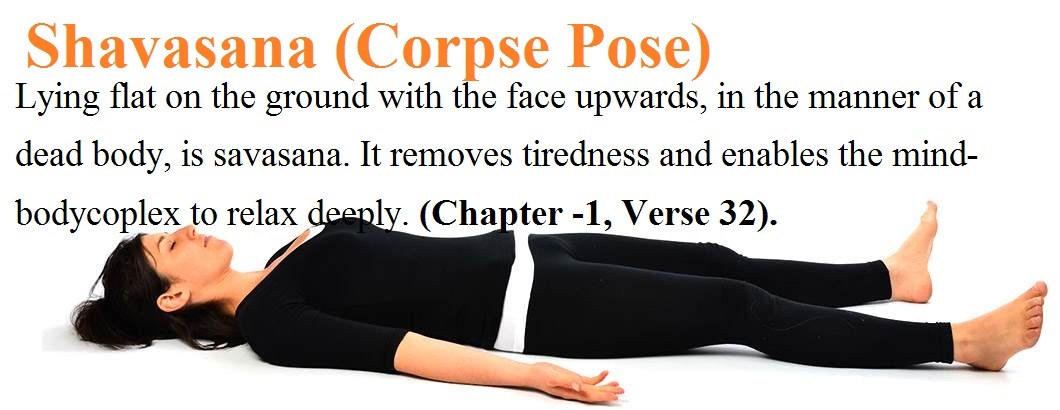
Shavasana (Corpse Pose) Uttanam sabavad bhumau sayanam tat savasanam/ Savasanam srantiharam chittavisrantikarakam//(Chapter -1, Verse 32). Lying flat on the ground with the face upwards, in

Paschimottanasana (Back Stretching Pose) Prasarya padau bhuvi dandarupau Dorbhyam padaghradvitayam ghrhitva/ Januparinyastalalatadeso Vasedidam paschimatanamahuh.// (Chapter -1, Verse 28). Stretching the legs in front on the
Padmasana (lotus pose) Vamorupari dakshinam cha charanam Samsthapya vamam tatha / Dakshorupari paschimena vidhina Dhrtva karabhyam drdham // Angghushthau hrdaye nidhaya Chibukam nasaghramalokayet / Etadvyadhivinasakari

Mayurasana (Peacock Pose) Dharam avashtabhya karadvayena Tatkurparasthapitanabhiparsvah/ Uchchasano dandavad utthitah san Mayuram etat pravadanti pitham//(Chapter -1, Verse 30). Lie down on the stomach, placing

Matsyendrasana (Spinal Twist Pose) Vamoru mularpitadakshapadam Janor bahir veshtitavamapadam/ Praghrhya tishthet parivartitangghah srimatysanathoditam asanam syat//(Chapter -1, Verse 26). Place the right foot at the

Kukkutasana (Cockerel Pose) Padmasanam tu samsthapya janurvorantare karau / Nivesya bhumau samsthapya vyomastham kukkutasanam//(Chapter -1, Verse 23). By adopting Padmasana, insert the hands between

Koormasana (Tortoise Pose) Ghudam nirudhya ghulphabhyam vyutkramena samahitah/ Kurmasanam bhavedetaditi yogavido viduh//(Chapter -1, Verse 22). Press the anus firmly with the ankles in the

Gomukhasana (Cow’s Face Pose) Savye dakshinaghulpham tu prshthaparsve niyojayet / Dakshineapi tatha savyam ghomukham ghomukhakrtih//(Chapter -1, Verse 20). Place the right ankle next to

Dhanurasana (Bow Pose) Padanghushthau tu panibhyam ghrhitva sravanavadhi / Dhanurakarshanam kuryad dhanurasanam uchyate//(Chapter -1, Verse 25). Holding the toes with the hands, pull them

Bhadrasana (gracious pose) Ghulphau cha vrshanasyadhah Sivantyah parsvayoh kshipet / Savyaghulpham tatha savye Dakshaghulpham tu dakshine // Parsvapadau cha panibhyam Drdham baddhva sunischalam / Bhadrasanam

Hatha Yoga Pradipika – Who can practice Yoga? Yuvo vrddhoativrddho va vyadhito durbaloapi va / Abhyasat siddhim apnoti sarvayogheshvatandritah//(Chapter -1, Verse -64). Either, Young or

Hatha Yoga Pradipika – Food conducive for Hatha Yogic Practices Ghodhuma-sali-yava-shashtika-sobhanannam / Kshirajyakhanda-navanitasi hamadhuni// Sunthipatolakaphaladikapanchasakam / Mudghadidivyam udakam cha yamindrapathyam//(Chapter -1, Verse -62). The most

Hatha Yoga Pradipika – Food Prohibited for Hatha Yogic Practices Katvamla-tikshna-lavanoshna-haritasaka / Sauvira-taila-tila-sarshapa-madya-matsyan // Ajadi-mamsa-dadhi-takra-kulattha-kola / Pinyaka-hingghu-lasunady-amapathyam-ahuh//(Chapter -1, Verse- 59). The foods which prohibited for

Hatha Yoga Pradipika -Moderate diet for Hatha Yogic Practices Susnighdhamadhuraharaschaturthamsavivarjitah / Bhujyate sivasamprityai mitaharah sa uchyate//(Chapter -1, Verse -58). Mitahara is defined as agreeable and
Electrocardiogram ECG: The ECG shows the heart’s electrical activity as line tracings on paper. It’s the recording of electrical activity of the heart. ECG is
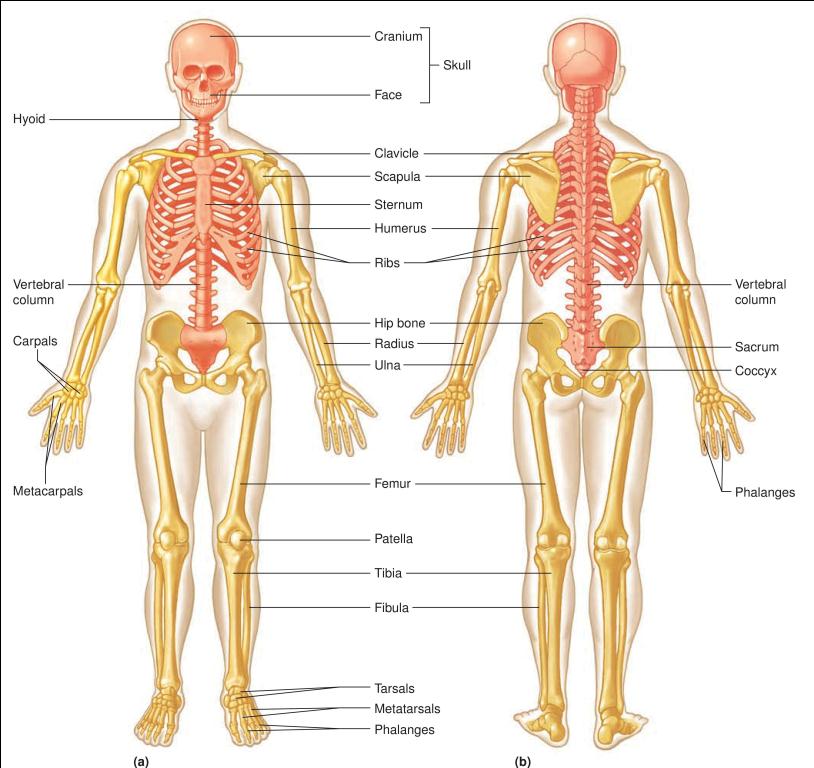
Functions of the Skeletal System? Support of the body Locomotion Provide protection for internal organs Act as a site for the production of blood cells,
Disorders of blood vessels: Arteriosclerosis: Arteriosclerosis is the thickening, hardening, and loss of elasticity of the walls of arteries. This process gradually restricts the blood
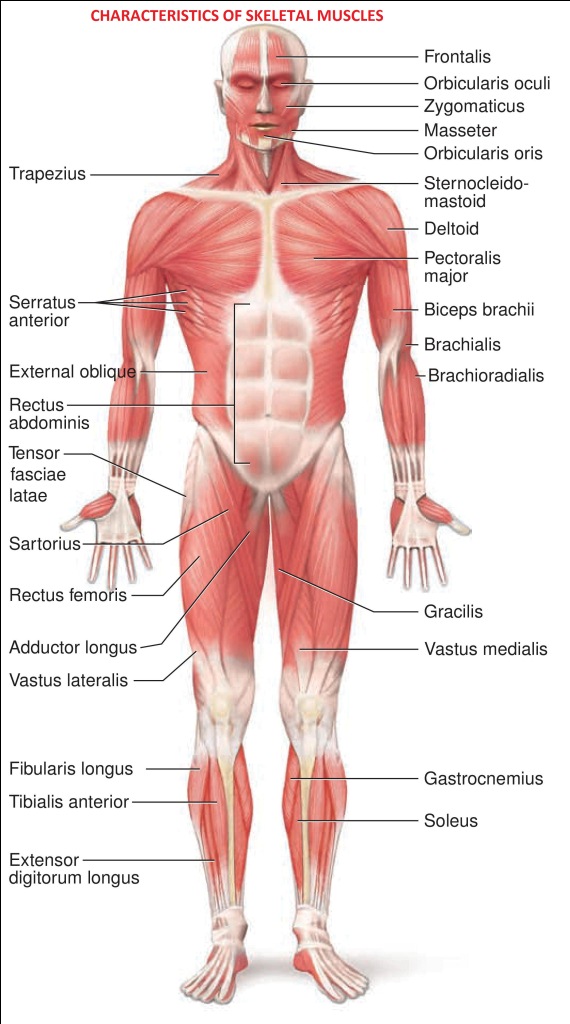
Properties of skeletal muscle: Excitability and irritability: It’s the property of a muscle to respond to a stimulus. If the response occurs in the front
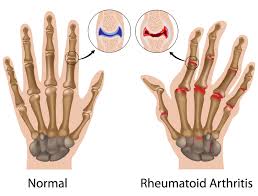
Joint Disorders Arthritis – inflammation of a joint. Characterized by pain, stiffness, and swelling. Over time, the joint can become severely damaged. Osteoarthritis is the
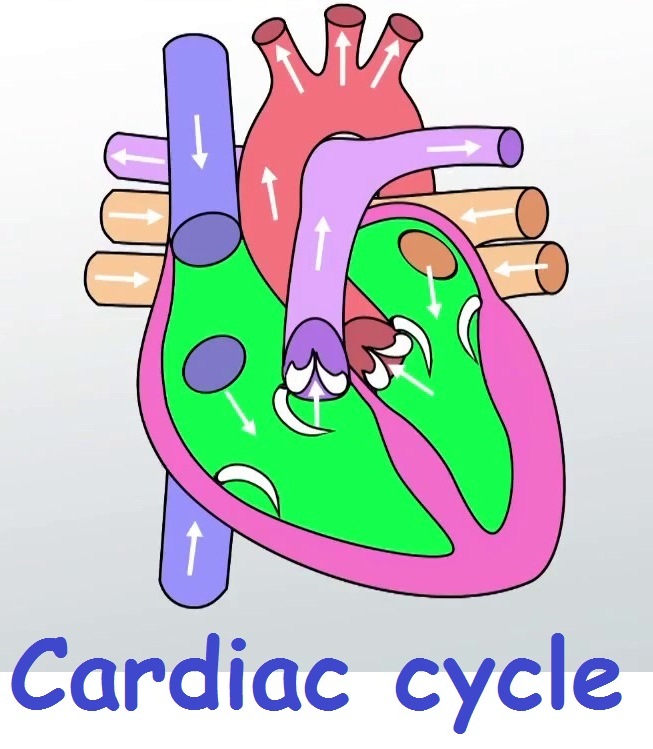
The Cardiac cycle: the function of the heart is to maintain a constant circulation of blood throughout the body. It acts as a pump
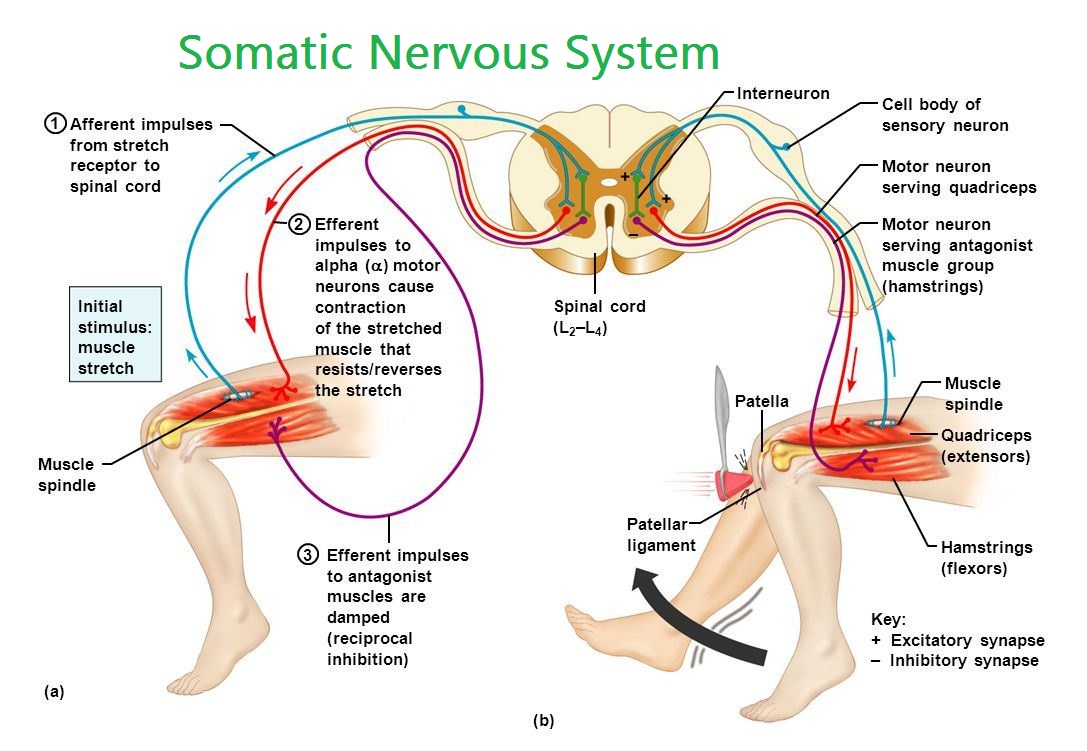
Somatic Nervous System The somatic system is the part of the peripheral nervous system that is responsible for carrying motor and sensory information both to
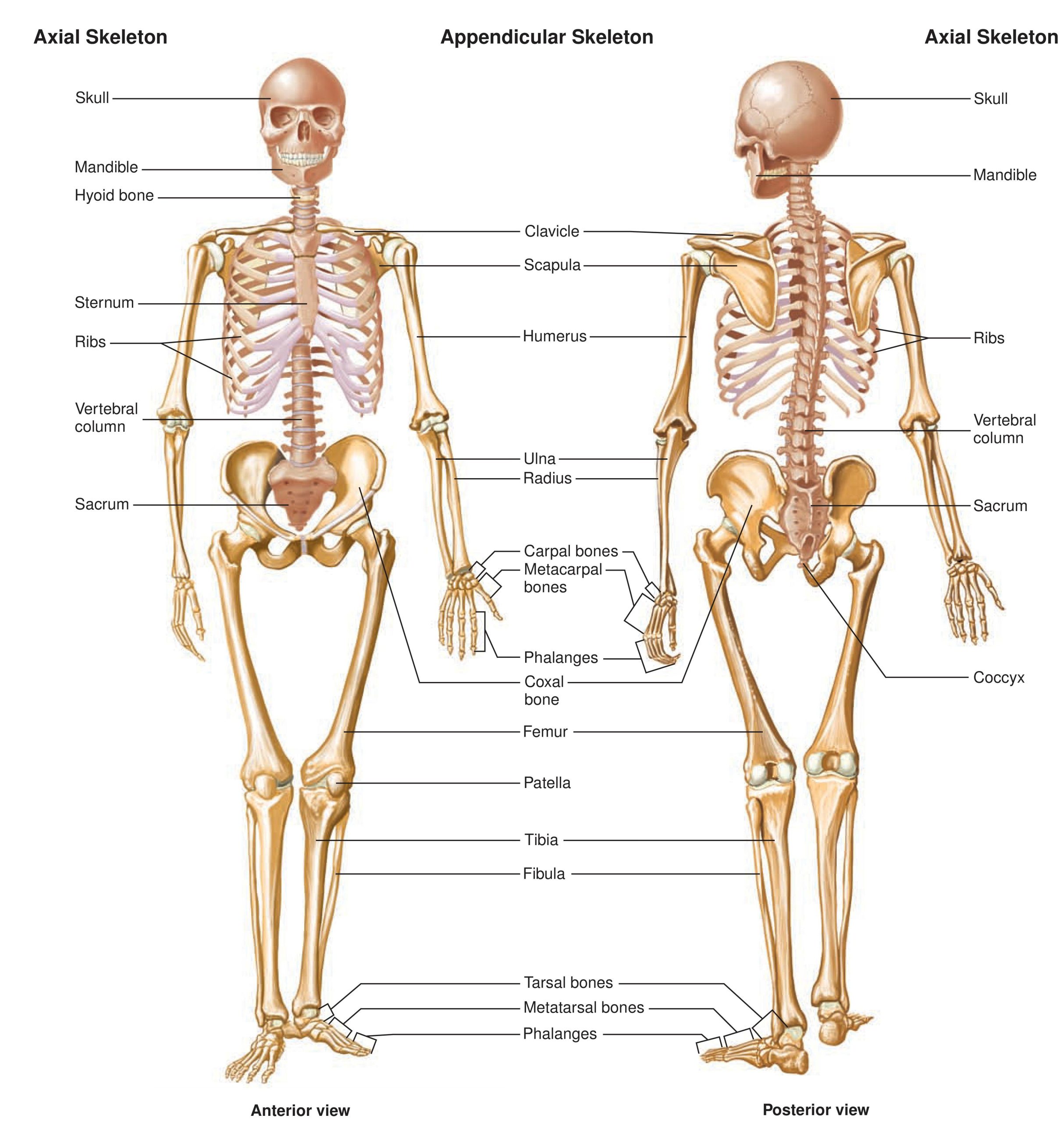
Skeletal system The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones making the human body a multifunctional structure. The skeletal system is composed of Bones,
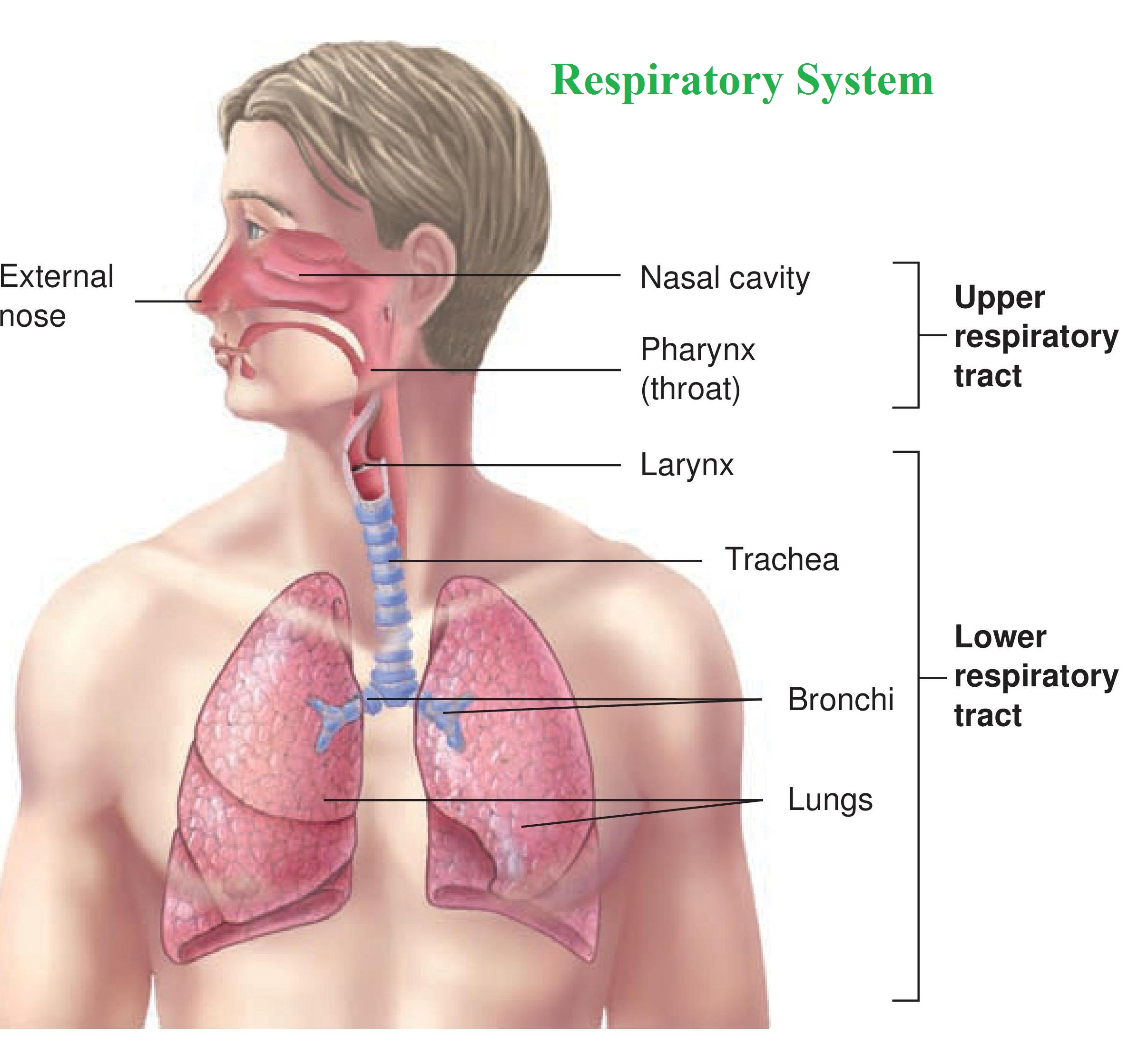
Respiratory system The Human Respiratory System is a series of organs which facilitates the diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream and distributes throughout the body
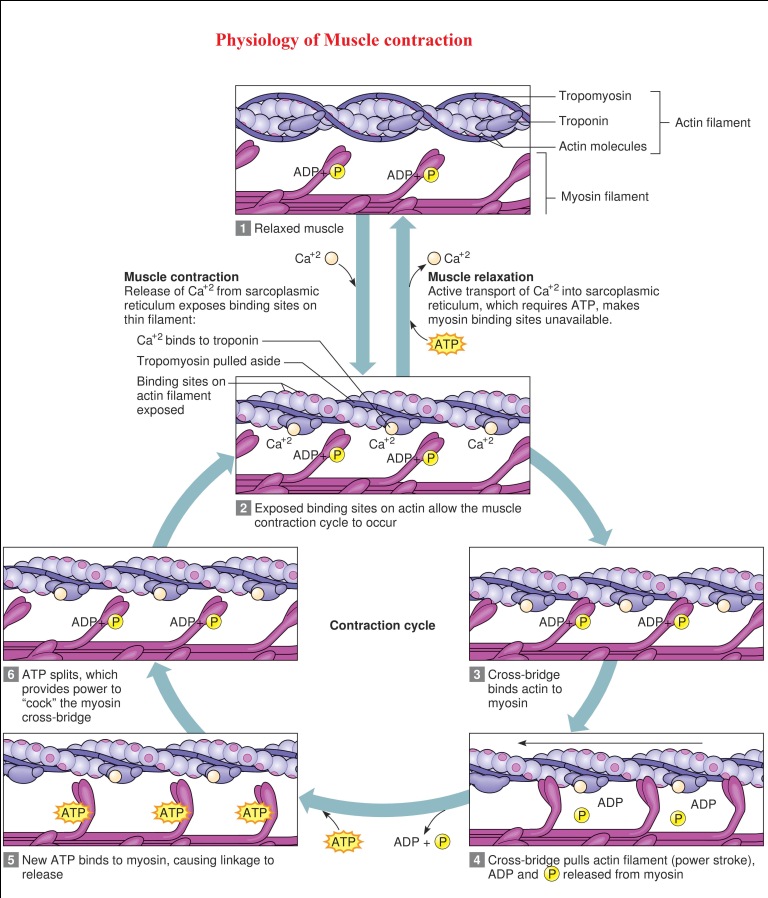
Physiology of Muscle contraction: Muscles contract to produce force, the actin and myosin filaments within the sarcomeres of muscle fibers bind to create cross-bridges and

Disorders of blood pressure Hypertension’s Hypertension is a rise in blood pressure above normal. It’s difficult to define the average normal blood pressure. It varies
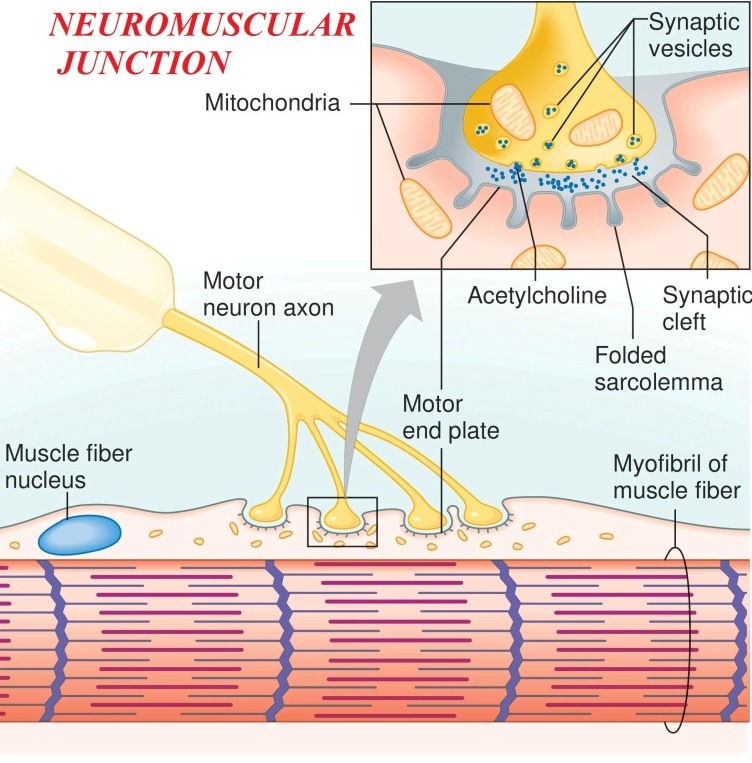
Neuromuscular junction (Myoneural junction) A neuromuscular junction is a synapse between a motor neuron and skeletal muscle. The space between the motor neuron and the
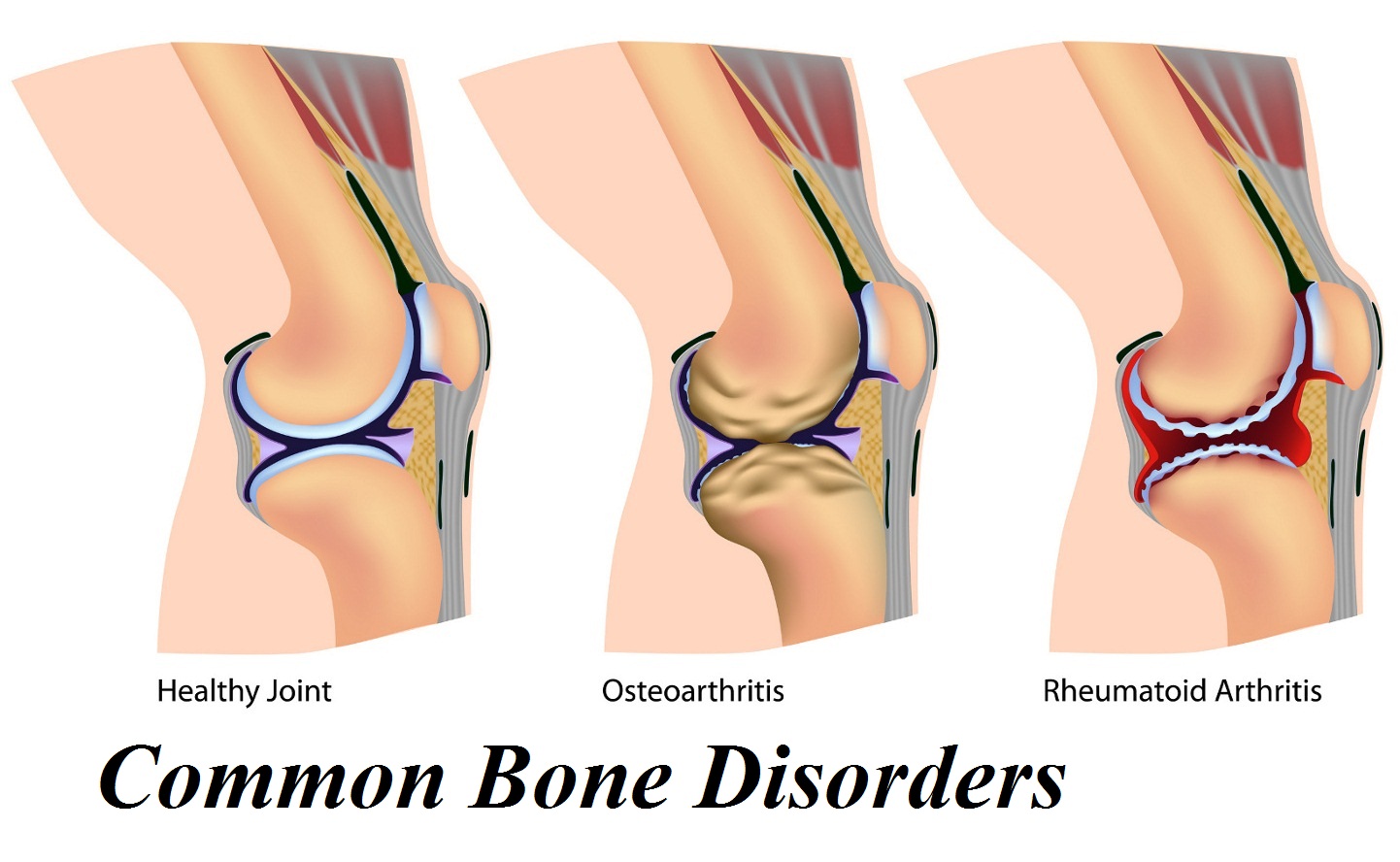
Common Bone Disorders Osteoporosis- Osteoporosis is a common disease that weakens bones, characterized with the prominent porous formation in the shaft or articulating part of
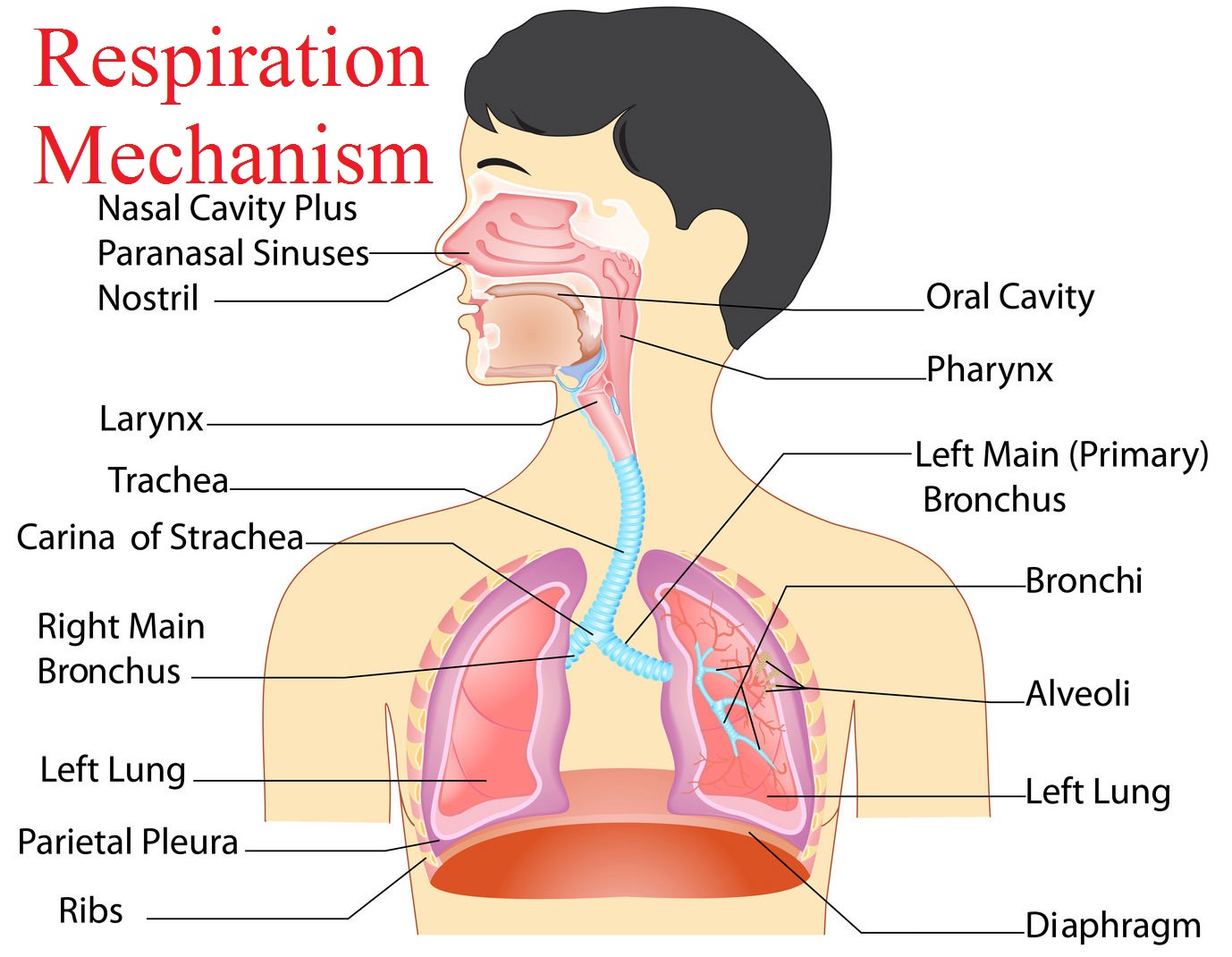
Respiration mechanism Normal breathing involves several different mechanisms. Shallow breathing is accomplished by the contraction of the diaphragm and the external intercostal muscles for inhalation.
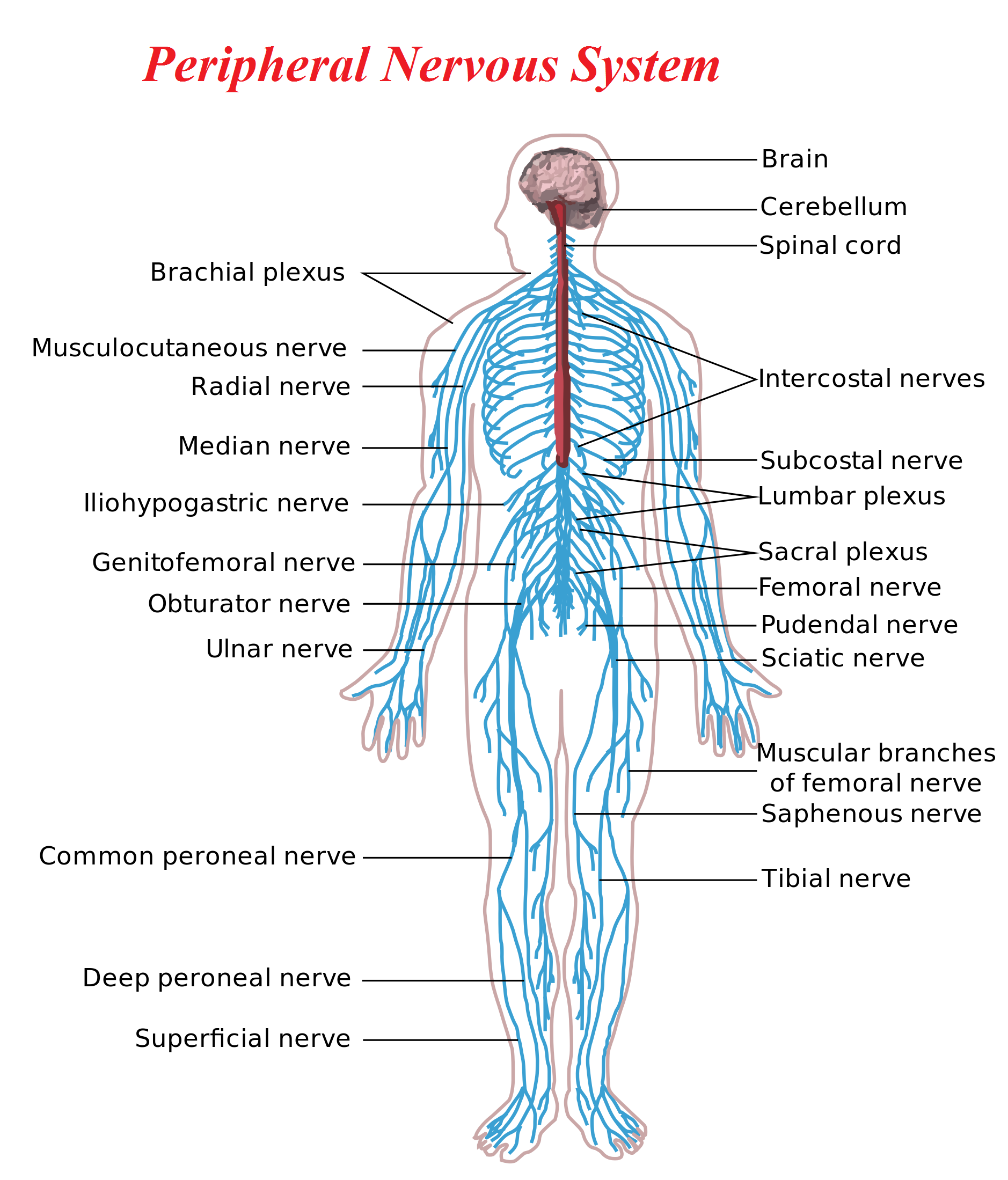
Peripheral Nervous System: The Peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the division of the nervous system containing all the nerves that lie outside of the central
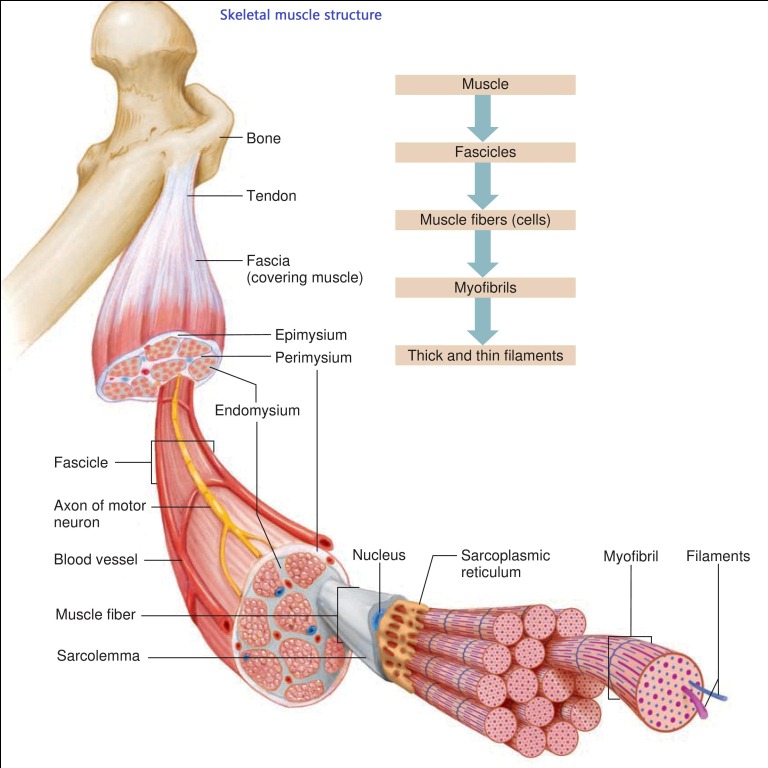
Skeletal Muscle Structure Skeletal muscles are composed of a large number of muscle fibers. Each muscle fiber has no one or more nuclei which lie
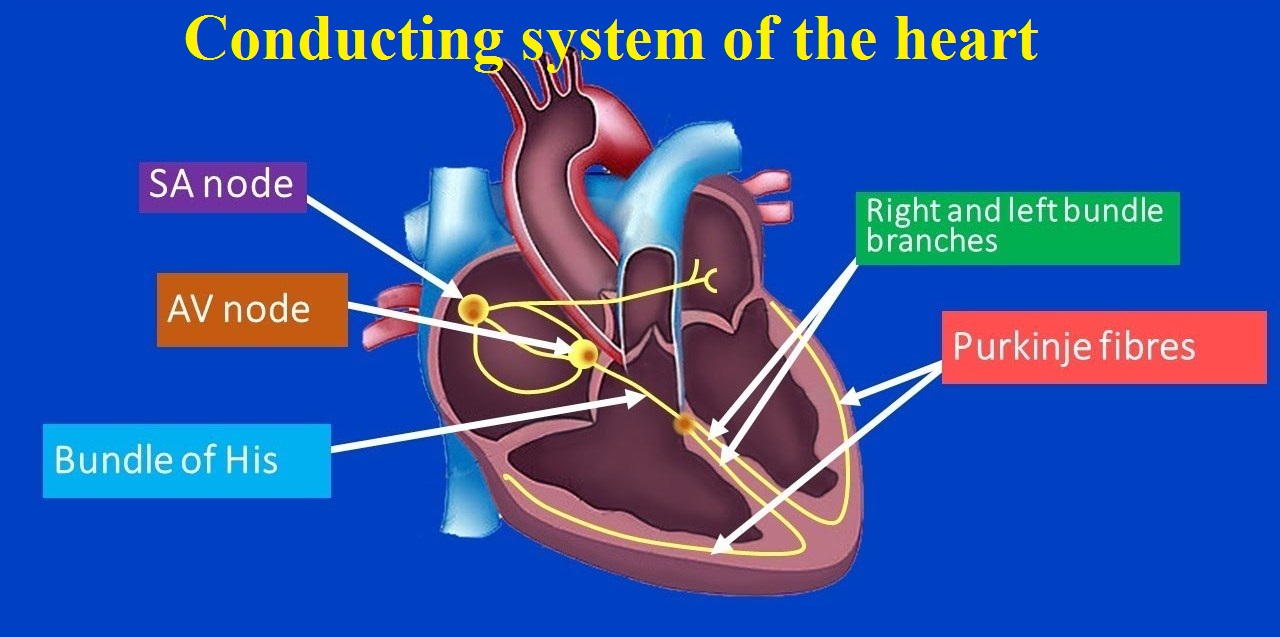
Conducting system of the heart Conducting system of the heart: the impulse for cardiac contraction is transmitted through the conduction system of the heart. This
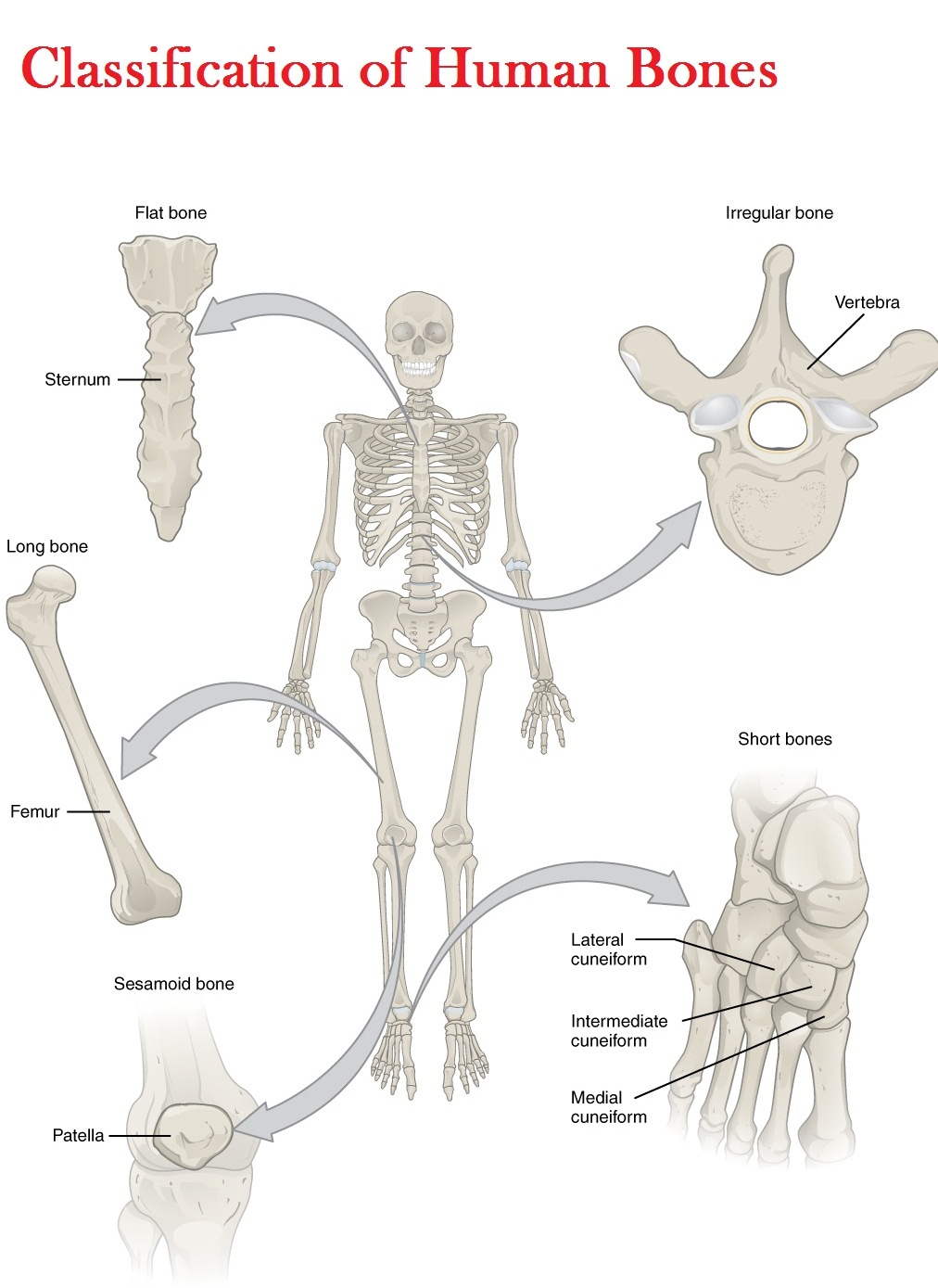
Classification of Bones according to shape Long bones: Long bones are characterized by a long tubular shaft and an articular surface at each end of
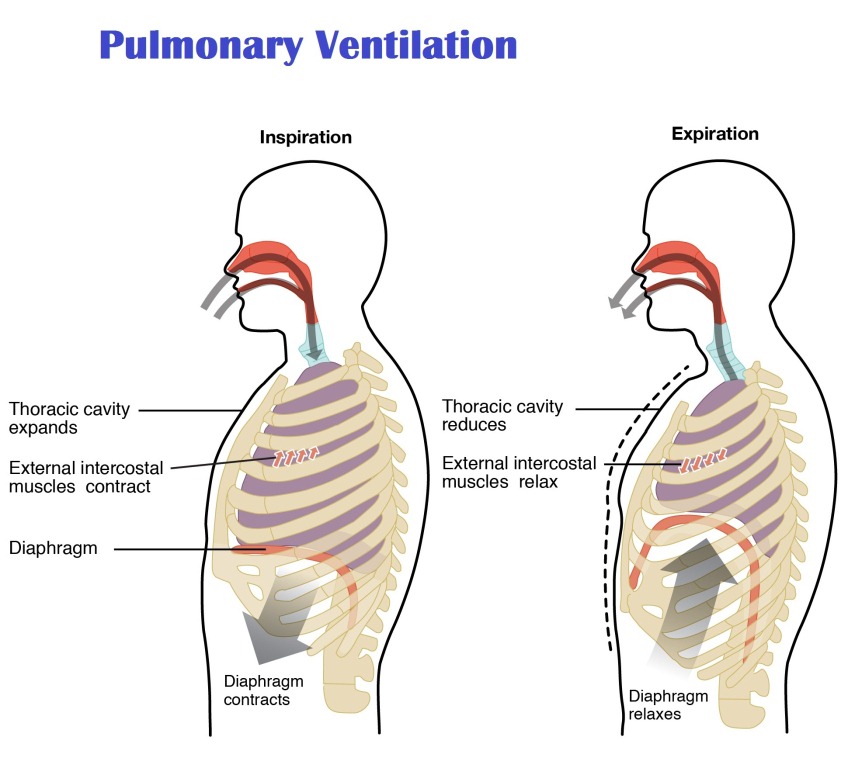
Pulmonary Ventilation Smooth muscle cells in the walls of the bronchioles adjust their diameter and help to control the flow of air into the alveoli
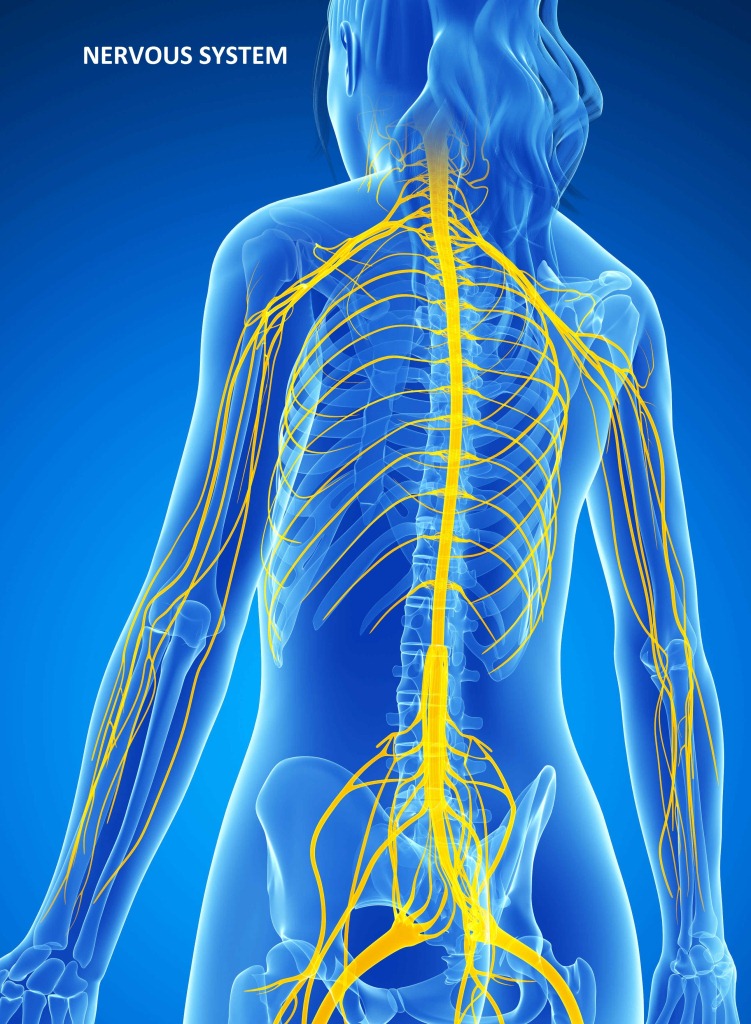
Nervous System The nervous system has been divided into two components: The central nervous system which is composed of the brain and the spinal cord,

CHARACTERISTICS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES The four major functional characteristics of skeletal muscle are: Contractility – The ability to shorten which causes movement of the structures
Social Chat is free, download and try it now here!