How you will manage Hypoventilation, by hatha yoga practices.
Hypoventilation refers to decreased breathing rate. It is characterized by slow, shallow breathing. This can be managed through pranayama practices like Bhastrika Pranayama,
Karuna Yoga Vidya Peetham Bangalore

Hypoventilation refers to decreased breathing rate. It is characterized by slow, shallow breathing. This can be managed through pranayama practices like Bhastrika Pranayama,
Hyperventilation refers to increased rate of breathing. It is characterized by rapid, deep breathing. This can be managed through pranayama practices like Ujjayi Pranayama, Nadi
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) describes a shortness of breath during sleep that comes on suddenly, causing the person to wake up gasping. Kechari Mudra Ujjayi
Refers to general shortness of breath, accompanies by tightness in the chest or feeling of suffocation. A few practices are as follows: Dhanurasana Jalaneti Shavasana
Shortness of breath/difficulty when lying down. A few practices are as follows: Ushtrasana Ardhamatsyendrasana Bhujangasana
Temporary stopping of breathing, especially during sleep. A few practices are as follows: Simhasana Nadi Shodana Pranayama Kechari Mudra
Total lung air Volume: The total lung air volume is about 4-6 litres. Residual volume: The amount of air that remains in the lungs at
Role of External intercostals muscles during inhalation. The contraction of the external intercostals and diaphragm is required for inhalation. Role of External intercostals muscles during
Unconscious control of breathing Unconscious control of breathing is maintained by the respiratory centre of the brainstem, which monitors the concentration of gases in the
A slow breathing rate keeps the heart stronger and better nourished, as it exerts a positive effect on the cardiac functions and coronary supply –
A few yogic practices to overcome shallow breathing are as follows: Kapalbhati Pranayama Bhastrika Pranayama Nadi Shodana Pranayama Ujjayi Pranayama

Define Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. It is the science that deals with the structures of the human body

As people of the 21st century, we hear a lot about the modern lifestyle we live and its undesirable effects on our health and society.

1. Flexion and Extension are movements that take place along the sagittal plane and involve anterior or posterior movements of the body. Flexion is an

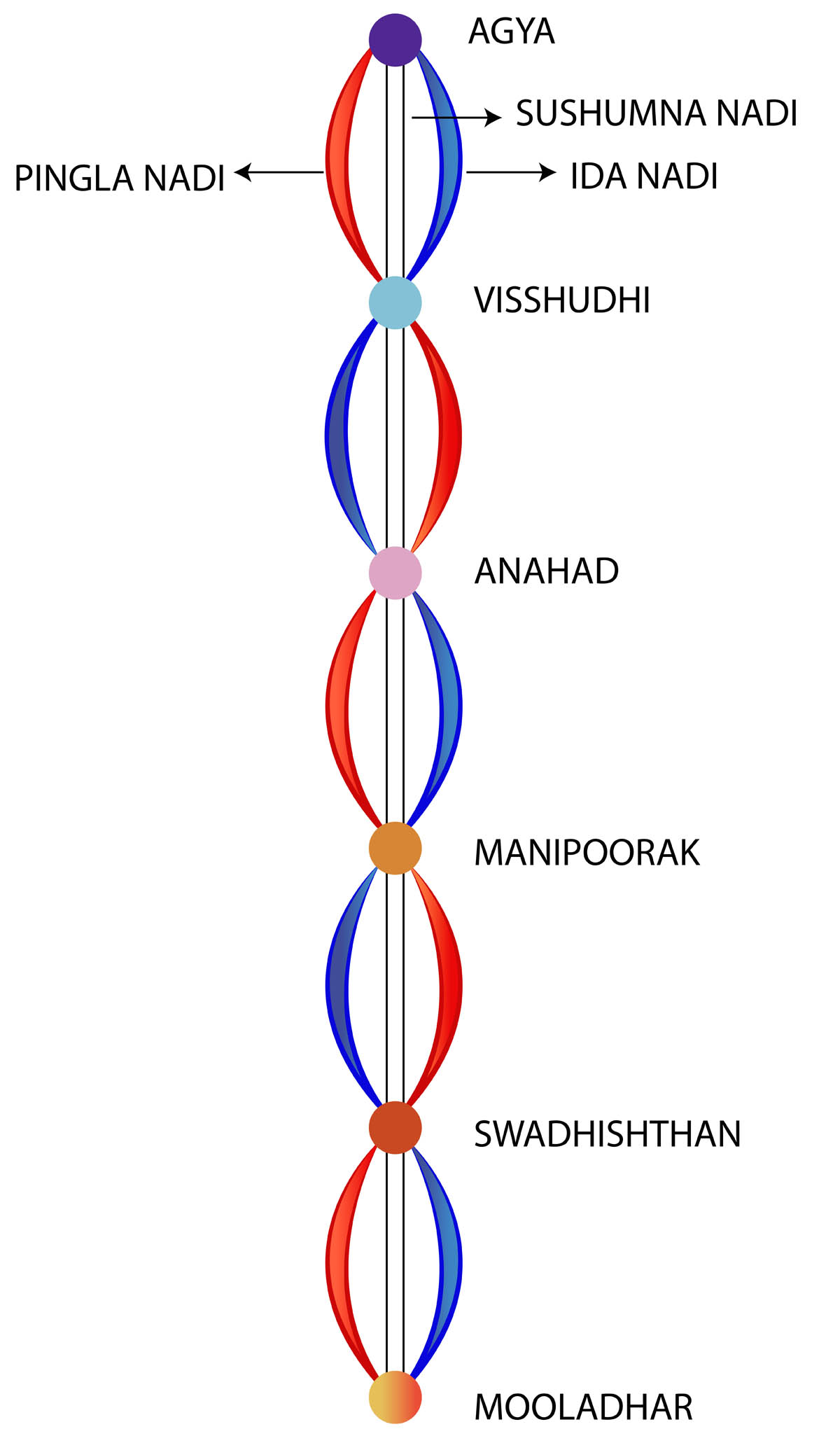
Mooladhara chakra (Root chakra) Lock in Brahma granthi Swadhisthana chakra (Sacral chakra) Karmic block, Desire for food and sex Manipura (Solar plexus chakra) Habits,
Visuddhi Chakra is violet in color, round, and has 16 petals. Vishudhi is the purification center and is known as the fountain of youth. Nectar

Guna is a Sanskrit term and means quality, peculiarity, or tendency. A Guna is a tattva or element of reality that can affect our psychological,

The Yoga text – Yoga Vasista, explains the diseases originating from stress and diseases which are not due to stress. Human emotions such as likes,

Purusartha is defined as the goal of human existence, the soul’s purpose, and the ultimate quest of life– the four aims of life. The four

Sattvic guna is a force favorable for the attainment of moksha. A sattvic mind is always steady and finds delight internally. Sattva guna is developed

Chaturvargas(four stages of life) i) Brahmacharya Ashram (1-25 years) student life, observing celibacy • Period of study and discipline • Period of probation • Students

1. Define Gaseous Exchange. [VP] – The transfer of gases between an organism and the external environment in either direction. It occurs by diffusion across

1. Why yoga student should know about “anatomy” Understanding yoga anatomy is crucial for all yoga students because it will increase the effectiveness of the asanas

Biomechanics of stretching 1. Isotonic contraction asana mechanism This is a type of contraction in which movement takes place, eg. When pushing or pulling an

Anatomical directional terminology Define the directional term “superior” Towards the head or top, eg. Head Define the directional term “cranial” Cranial refers to the skull

Chakras with a number of petals Mooladhara chakra (Root chakra) Four Swadhisthana chakra (Sacral chakra) Six Manipura (Solar plexus chakra) Ten Anahata (Heart chakra) Twelve

Yoga Injuries and How To Prevent Them Some of the common contraindications of asana practice are as follows: High BP and cardiac conditions: People with

Qualification: Ashtanga Surya Namaskar can be practiced by anyone whose physical and mental health or rather overall well-being is sound. Contraindications: Ashtanga Surya Namaskar should

The steps involved in, the basics arc structure of class. Most yoga classes follow a basic arc structure that includes the following five elements: a)

60 min hatha yoga sequence for both gender for the age group of 25 to 40, who does not have any physical or mental illness.
60 min vinyasa yoga practice list and sequence it. Both gender for the age group 25 to 40. Warm-Up (10 mins) Supta virasana with cushion

60 min practice list and sequence – back pain issue, slip disc, and sciatica. Centering (2 mins) Om chanting (2 mins) (3 times) Pranayama (3

60 min practice list and sequence – cardiac problem Centering (2 mins) Om chanting (2 mins) (3 times) Pranayama (5 mins) Nadi Shodhana (long inhale

Eccentric Downward movement of joint. Tension is produced when the muscle lengthens. Concentric Upward movement. Tension is produced when the muscle shortens. Causes joint movement.

This is a contraction in which movement does not take place, because the tension generated by the contracting muscle exceeds the load on the muscle.

This happens without oxygen, fuel comes from muscle storage and is short, highly intense and burns fat directly. Example is weightlifting. More fast twitch muscle

This takes place with oxygen where carbohydrate and oxygen are used as fuel for the first two minutes after which fat is burned. These are

The greater your aerobic capacity, the longer your muscles can function without fatiguing or burning out. Type IIa fibers have more potential for increased aerobic capacity,

Slow-twitch, or Type I muscle fibers, are skeletal muscle fibers that slowly contract. Slow-twitch muscle fibers support everyday actions, like standing from a seated position and

Hamstring muscles are in the back of the thigh, starting at the hip and inserting to the knee. The three hamstring muscles are: Biceps femoris, closest to