
quadriceps muscles
The quadriceps are a group of muscles present on the front of the thigh. They consist of four distinct muscles: the rectus femoris, the vastus lateralis,
Karuna Yoga Vidya Peetham Bangalore


The quadriceps are a group of muscles present on the front of the thigh. They consist of four distinct muscles: the rectus femoris, the vastus lateralis,

Vital capacity (VC) is the maximum amount of air a person can inhale after a maximum exhalation. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve
The pleura fluid itself has a slightly adhesive quality that helps draw the lungs outward during inhalation rather than slipping round in the chest cavity. In
The transfer of gases between an organism and the external environment in either direction. It occurs by diffusion across a concentration gradient and includes the

Moving the scapula toward the spine, also called scapular adduction or pulling the mandible backward. When you draw your shoulder blades together, it’s a retraction,

Explain term Protraction, in compare with asana movement. Moving the scapula away from the spine, also called scapular abduction or jutting the mandible forward. When
Explain term Lateral rotation (external rotation), in compare with asana movement. Lateral rotation is rotating away from the midline. An external rotation is when the
Explain term Medial rotation (internal rotation), in compare with asana movement. Medial rotation is rotating toward the midline. Medial rotation is a term describing a
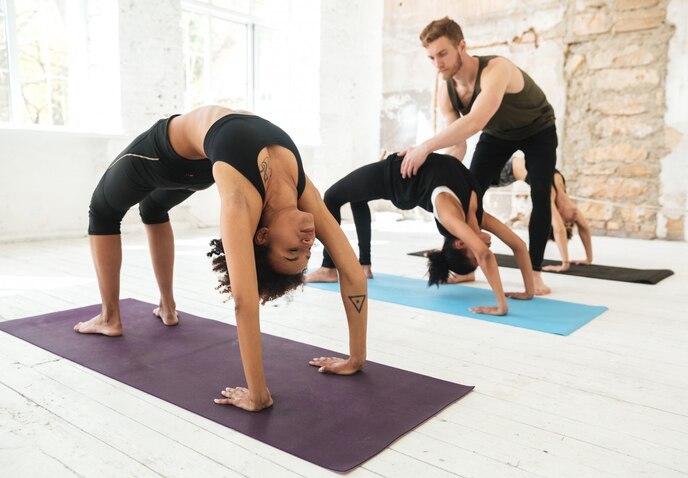
Lateral flexion is a movement that bends the body to the right or left side. It helps to open up the side-body, strengthens the obliques,

Turning the palms of the hands downward, or walking on the inside edge of the foot. Pronation describes a rotational movement of the forearm that results

Turning the palms of the hands upward, or walking on the outer edge of the foot. Supine means lying in a faceup position. It is

Adduction of a joint makes a body part move towards the midline of the body. For instance, adduction happens when we move the thigh toward or

Abduction of a joint makes a body part move away from the midline of the body in the anatomical position. For instance, abduction is the term
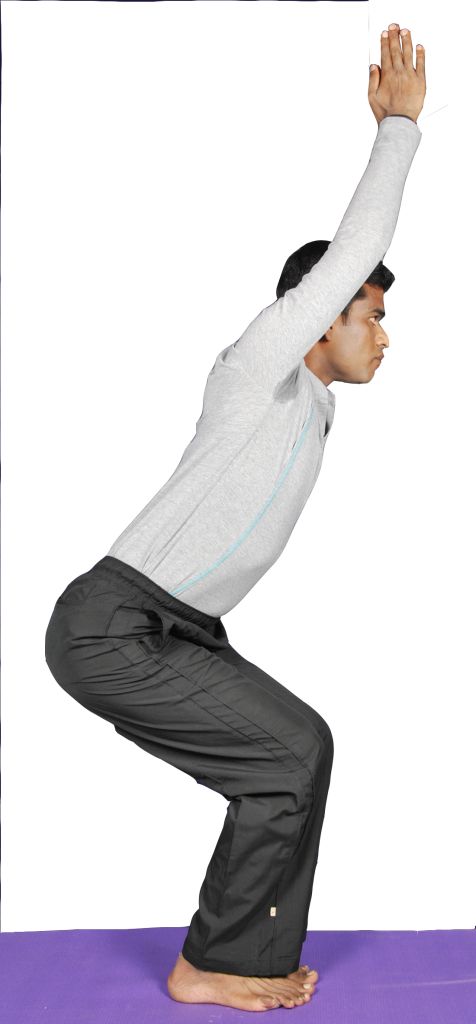

Extension is an increase in the angle of a joint. Extension of a joint makes a body part move in a backwards direction. (The knee

Flexion of a joint makes a body part move in a forward direction from the anatomical position. Flexion is a movement that brings the spine down
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between moving parts in your body’s joints. Elbow bursitis is inflammation or irritation of the bursa (shown in

Fascia is made up of sheets of connective tissue that is found below the skin. These tissues attach, stabilize, impart strength, maintain vessel patency, separate muscles,
A ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.

A tendon is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone. Tendons may also attach muscles to structures such as the eyeball. A tendon serves
Cartilage is the main type of connective tissue seen throughout the body. It serves a variety of structural and functional purposes and exists in different types

This is a contraction in which movement does take place, because the tension generated by the contracting muscle exceeds the load on the muscle. This

This is a contraction in which no movement takes place, because the load on the muscle exceeds the tension generated by the contracting muscle. This

Anaerobic is performed in the absence of oxygen at a maximal intensity that can only be sustained for a short period of time due to
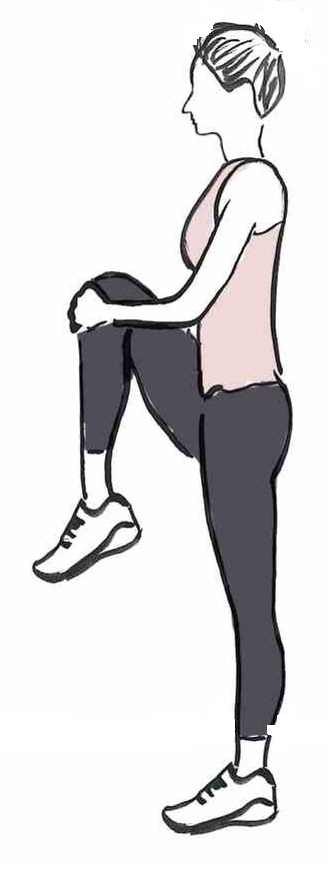
Aerobic exercise is performed in the presence of oxygen at a submaximal intensity over a prolonged period of time, e.g. rowing. Yoga is necessary to

Anaerobic is performed in the absence of oxygen (It uses carbohydrate and minimal oxygen) at a maximal intensity that can only be sustained for a
Aerobic yoga is a style of yoga in which the asanas — yoga postures — are sequenced together much faster than they ordinarily would be, in

Fast twitch muscle fiber (type -2), with hatha yoga practices. These are designed for anaerobic exercise and produces large amount of force in a very

slow twitch muscle fiber (type -1), with respective hatha yoga style. A type of muscle fibre associated with aerobic work. It produces a small force

The motor neurons release a chemical, which is picked up by the muscle fibre. This tells the muscle fibre to contract, which makes the muscles

major skeletal muscles. Coracobrachialis Biceps brachii Quadriceps femoris Triceps brachii Anconeus Pronator teres Flexor carpi radialis Palmaris longus Thyroarytenoid Rotatores

general benefits of hatha yoga practices on respiratory system. Practice of hatha yoga which is a combination of asanas (physical postures) and Pranayama (Yogic breathing

Why we should breathe in nose, why not in mouth. Nose breathing is more beneficial than mouth breathing. Breathing through your nose can help filter out

Breathing not only provide your body with necessary oxygen, but it also removes the waste like carbon dioxide. To get rid of carbon dioxide, your

What is the breathing pattern we should adopt for twisting asana? Exhale when twisting asana

What is the breathing pattern we should adopt for lateral bending asana? Exhale when moving into side bends.

breathing pattern we should adopt for forward bending asana? Exhale when forward bending during asana practice.

Hypoventilation is breathing that is too shallow or too slow to meet the needs of the body. If a person hypoventilates, the body’s carbon dioxide

Practices such as Sun salutation, asanas (e.g., bridge pose, …), pranayama (Nadi shodana, kapalabati), conscious effort and mindfulness practices can help to overcome shallow
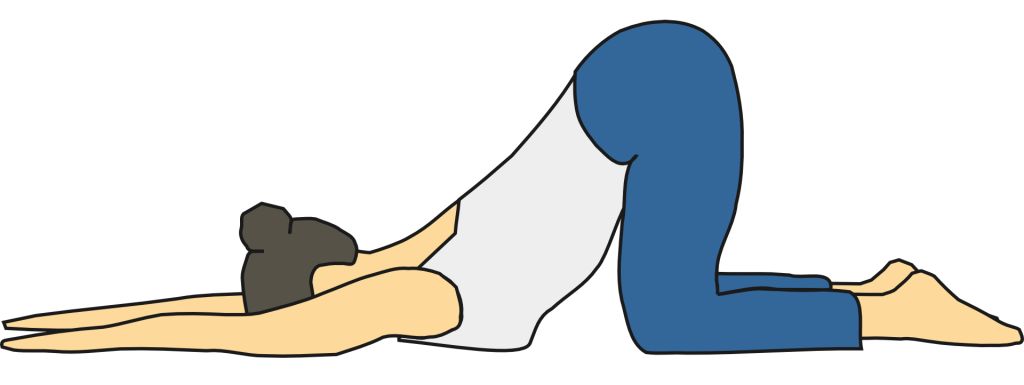
Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges. This contraction creates a vacuum, which pulls air into the lungs. Upon

The right lung consists of three lobes: the right upper lobe (RUL), the right middle lobe (RML), and the right lower lobe (RLL)