Parivartan Mudra (Transformation Gesture)
Introduction
Parivartan Mudra, also called the Transformation Gesture, is a yogic hand gesture used to channel energy for change, renewal, and balancing bodily and mental functions. It is often incorporated into meditation, pranayama, and mudra therapy to facilitate physical detoxification, emotional release, and mental clarity.
This mudra helps practitioners redirect pranic flow, release stagnation, and promote overall harmony.
Meaning
Etymology:
Parivartan means transformation, change, or rotation in Sanskrit.
Mudra means gesture or seal.
Symbolism:
Represents change, renewal, and energetic transformation.
Encourages mental clarity, emotional flexibility, and adaptability.
Symbolically removes blockages and restores balance in mind and body.
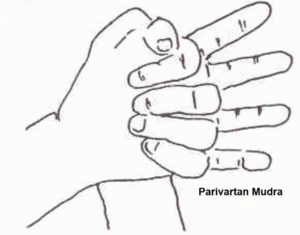
How to Perform Parivartan Mudra
Lie down on your back. Clasp your hand tightly, interlocking the fingers.
Then with the fingers of the left-hand press on the back of the right hand and vice versa. Repeat 27 times.
Benefits
Facilitates detoxification and energy flow throughout the body.
Improves mental clarity, focus, and decision-making.
Reduces stress, emotional stagnation, and mental fatigue.
Enhances flexibility and adaptability in body and mind.
Balances prana and subtle energy channels.
Supports self-awareness, transformation, and personal growth.
Contraindications
Avoid if there is injury or pain in hands, fingers, wrists, or elbows.
People with arthritis or joint limitations should practice gently.
Stop practice if discomfort or strain occurs.
Anatomy & Physiology
Involves phalanges, interphalangeal joints, intrinsic hand muscles, and forearm muscles.
Stimulates median and ulnar nerve endings, enhancing sensory perception and cortical activity.
Improves circulation in hands, forearms, and upper extremities.
Promotes postural alignment and muscle relaxation, facilitating deeper breathing and pranic flow.
Kinesiology
Isometric contraction of thenar, hypothenar, and interossei muscles maintains finger interlock.
Engages forearm, shoulder, and upper back muscles, improving posture and stability.
Enhances fine motor coordination, proprioception, and hand awareness.
Supports mind-body integration through intentional hand positioning and focus.
Neurology
Activates median, ulnar, and radial nerves, stimulating the somatosensory cortex.
Promotes parasympathetic nervous system activation, reducing stress and fostering calmness.
Visualization of transformation strengthens neural pathways associated with adaptability, emotional resilience, and energy flow.
Duration of Practice
Beginners: 5 minutes daily.
Intermediate/Advanced: 10–15 minutes, once or twice daily.
Ideal during meditation, pranayama, or energy-balancing sessions.
Counter Mudra
Prana Mudra or Gyana Mudra can serve as counter mudras to energize and stabilize after transformation practice.
Alternating Parivartan Mudra with these mudras balances dynamic energy with calm awareness.
Conclusion
Parivartan Mudra is a powerful gesture for transformation, energy balance, and mental clarity. Regular practice enhances adaptability, emotional resilience, and prana flow, making it an effective tool in meditation, pranayama, and yoga therapy.
FAQ
Q1: Can Parivartan Mudra help with emotional stress?
A1: Yes, it facilitates release of stagnation and promotes emotional balance.
Q2: Can beginners practice it safely?
A2: Yes, starting with 5 minutes daily is sufficient, gradually increasing duration.
Q3: Is visualization important?
A3: Visualization enhances the effects, but mindful hand placement and breathing are also effective.
Q4: Can it be combined with other mudras or yoga asanas?
A4: Yes, particularly with pranayama and detoxifying asanas for optimal energy flow.
References
Swami Satyananda Saraswati, Mudras for Healing and Transformation, Bihar Yoga Publications, 2012.
Dr. Harish Johari, Mudra: The Gateway to Health, Inner Traditions, 1994.
B.K.S. Iyengar, Light on Yoga, HarperCollins, 2005.
Yoga Journal, Mudras for Energy, Transformation, and Focus, 2018.
Hatha Yoga Pradipika and yogic texts on energy channels, prana flow, and meditation practices.