Function of diaphragm in respiration
Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges. This contraction creates a vacuum, which pulls air into the lungs. Upon exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its domelike shape, and air is forced out of the lungs.
Pros and cons of dynamic and isometric static hatha yoga style with example.
Pros and cons of dynamic and isometric static hatha yoga style with example. Dynamic Hatha Yoga: Typically done by people who are just beginning with the practice of yoga. As it is dynamic it involves a continuous flow of movement filled with energy. It is heat-producing and helps in bedding strength and flexibility. Dynamic practices […]
3 myths about Yoga, Bio-Mechanism & posture alignment

How important is bio-mechanism education for yoga teachers? The bio-mechanism is the science of movement. It includes the study of all physiological mechanisms of the body. The study of kinetics is important in educational disciplines such as rehabilitation therapy, sports medicine, exercise, biomechanics, and orthopedics. Since Hatha Yoga is based on movement, it makes sense […]
Isometric and Isotonic (pose) Yoga Asana
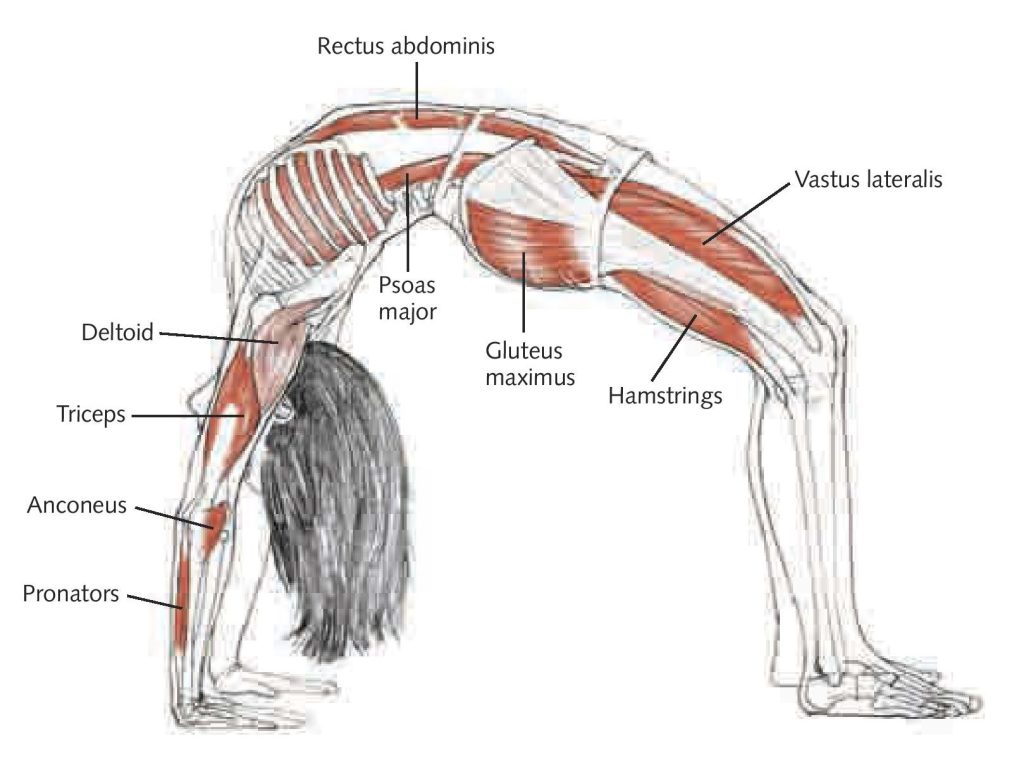
Isometric – no movement, muscles stay the same length. Example, staying in plank position, not moving. Isotonic: i.e. eccentric and concentric Eccentric muscle moves to lengthen, resisting gravity i.e. forward fold into Uttanasana. Concentric, muscle moves to shorten, moving against gravity. Example, moving from chaturanga dandasana to plank position.
Three Types of Muscle Contractions (Isometric, Concentric, and Eccentric)
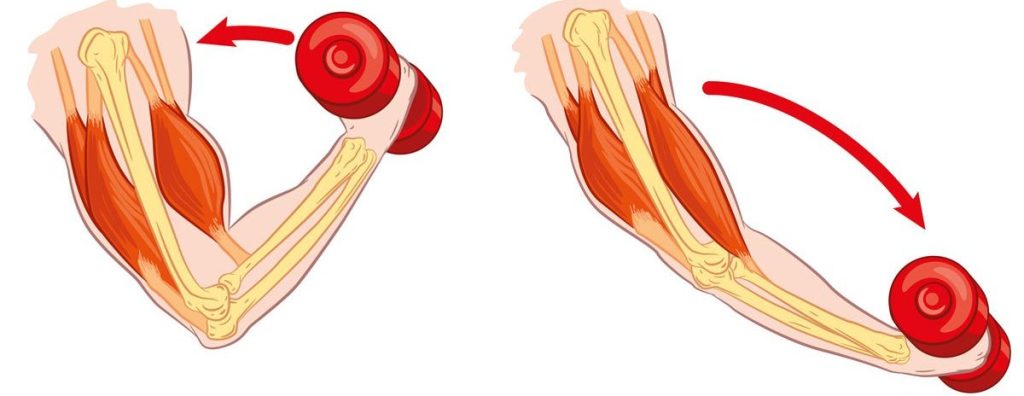
1) Isometric Muscles are tense but no joint movement. 2) Isotonic Eccentric Downward movement of joint. Tension is produced when the muscle lengthens. Concentric Upward movement Tension is produced when the muscle shortens. Causes joint movement.
Aerobic and Anaerobic Yoga Pose

Aerobic activity This takes place with oxygen where carbohydrate and oxygen are used as fuel for the first two minutes after which fat is burned. These are lower intensity activities. More fat for energy is used and leads to a better ability to burn fat. Blood vessels increase and become bigger to accommodate the oxygen […]
Muscle Fiber Types: Fast Twitch Muscle Fiber and Slow Twitch Muscle Fiber
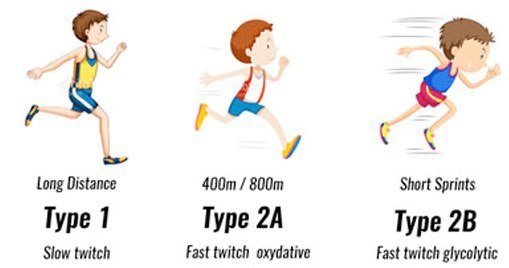
Slow Twitch Muscles that are associated with aerobic work are called slow twitch. These are the muscles working when we do the simpler yoga poses. Small force is produced over a sustained period. It is suited for endurance activities such as running marathons. Fast Twitch These fibres are associated with anaerobic activity. They are […]
Yoga & Its Stretching Mechanism
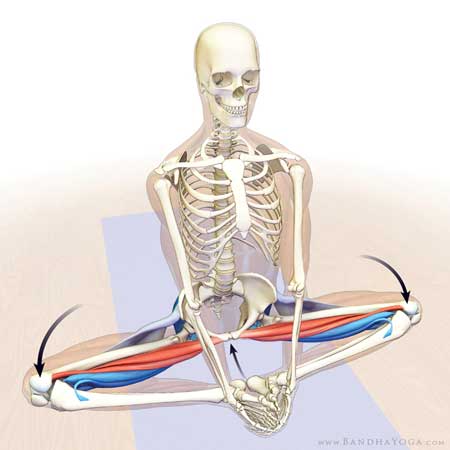
Yoga & Its Stretching Mechanism Stretching can facilitate mobility, improve muscle mechanics. Definition and goal of stretching Stretches is specific positions sustained to increases and maintain the length of a muscle or a muscle group. It lengthens tendons, warms up ligaments, and prepares joints for work. As a result, there is: Additional flexibility throughout […]
Physiology of Muscle contraction
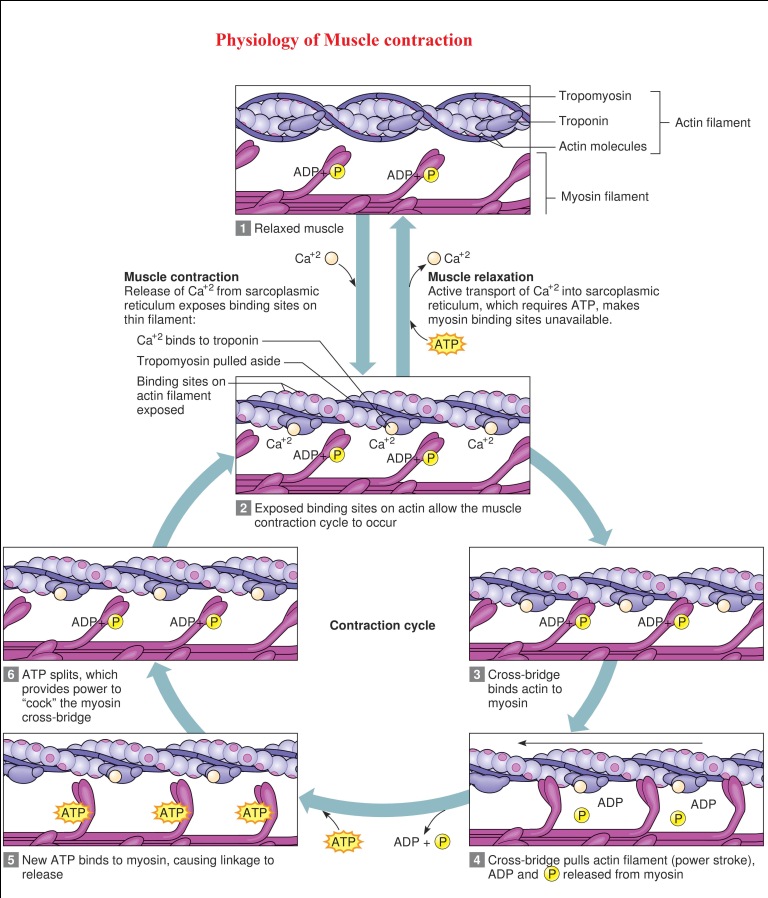
Physiology of Muscle contraction: Muscles contract to produce force, the actin and myosin filaments within the sarcomeres of muscle fibers bind to create cross-bridges and slide past one another, creating a contraction. The events of muscle contraction: During a normal resting state of a muscle, the muscle membrane is in a polarized state, this occurs […]
Disorders of blood pressure
Disorders of blood pressure Hypertension’s Hypertension is a rise in blood pressure above normal. It’s difficult to define the average normal blood pressure. It varies from one age group to other. The blood pressure in an adult may be 120/80. Hypertension has a strong relation with life style regardless of gender and socio-economic status. The […]
