50 Hrs – Mudra & Pranayama Teacher Training Certificate Course
Contact Hr – Direct or live interaction with Teacher. This includes in-person or real-time online sessions where you are actively engaged with the teacher, receiving instruction, feedback, and guidance.
Non-Contact Hr – Reading a book or article, or watching a video, Self-Practice, Written Assignment, Project Work, Audio Assignment, Video Assignment.
- Duration: 50 Hours
- Contact Hours: 40 Hours
- Non-Contact Hours 10 Hours
- Total Fee for the Training(For Indian Citizens Only): INR 20,000(Registration Fee) + INR 45,000 (Course Fee) = INR 65,000
- Total Fee for the Training(For Non-Indian Citizens Only): USD 300(Registration Fee) + USD 550 (Course Fee) = USD 850
- Accreditation: Yoga Alliance USA YACEP.
- Skill level: Beginners, Intermediate & Advanced
- Language: English
- Mode: Offline/Online/Hybrid/Self-Paced
- About the course facilitator: Dr. S. Karuna Murthy, M.Sc., Ph.D., E-RYT 500, YACEP
- Language: Our courses will be held in English Medium.
- Course Dates: Please Contact Us (karunaayoga@gmail.comor +91 9686549129)
Mudra and Pranayama Certificate Course
Yoga has become synonymous with term Asana; however the entire practice of Yoga is based on practices of consciousness. Asana, Pranayama, Mudra and Bandhas are the three most important techniques that lead to the state of higher level of meditation. When these four techniques are done with awareness, knowledge and preparation, Yoga becomes possible. In this journey to self-discovery, pranayama leads to the purification of senses, prana and mind. With a consolidated state of mind one attains Mudra and maintains bandhas in order to maintain one pointed awareness. Learn these four important practices in Yoga and let your practice be to attain the state of Yoga itself.
practices of consciousness. Asana, Pranayama, Mudra and Bandhas are the three most important techniques that lead to the state of higher level of meditation. When these four techniques are done with awareness, knowledge and preparation, Yoga becomes possible. In this journey to self-discovery, pranayama leads to the purification of senses, prana and mind. With a consolidated state of mind one attains Mudra and maintains bandhas in order to maintain one pointed awareness. Learn these four important practices in Yoga and let your practice be to attain the state of Yoga itself.
Pre-requisites:
- This course is open to all students who wish to deepen their knowledge and application of some of the highest teachings of
- Participants do not need to be yoga
- Mastery of any yoga practice is not
- Only yours sincere desire for knowledge and your commitment to personal
- Love for Yoga is the most important eligibility factor for learning this course.
- Students who want to know Yoga in totality and move beyond Pranayama,& Mudra.
What do I need for the online course?
- Yoga mat
- Computer / Smartphone with camera
- Internet connection
- Yoga Blocks
- Pillow or Bolster or Cushion
- Strap
- Notebook and Pen
- Zoom
Assessment and Certification
The students are continuously assessed throughout the course at all levels. There will be a written exam at the end of the course to evaluate the understanding of the philosophy of Yoga and skills of the students. Participants should pass all different aspects of the course to be eligible for the course diploma.
Recommended Texts
- Asana Pranayama Mudra Bandha by Swami Niranjananda Saraswati
- B.K.S. Iyengar, Light On Yoga.
What’s the language of the course?
Our courses will be held in English Medium.
What is Mudra Teacher Training
Mudra means ‘seal’ or ‘Gesture’ and also medical science believes circuit by pass. It is a branch of ancient yogic science like Hatha Yoga. It has been mentioned that Mudras are more powerful than asanas and Pranayama. Several Mudras can be practised to regulate , several involuntary, physiological and biochemical activities . Today Mudra is used to cure illness, to balance body and mind.
Mudras are essential to yoga, meditation, and various Indian classical dances. They are believed to have the power to evoke specific states of mind or to bring about physical, emotional, or spiritual benefits. In this sense, mudras can be an essential tool for promoting physical and mental well-being, as well as for spiritual growth and self-realization.
In yoga and meditation, mudras are often used to focus the mind and facilitate energy flow within the body. By using specific hand gestures, practitioners can direct the flow of energy to specific areas of the body, which may help to improve physical and mental well-being.
In Indian classical dance, mudras convey specific emotions, stories, or themes. Precise hand gestures, facial expressions, and body movements help to tell a story or convey a particular message.
Overall, mudras are essential to various spiritual and cultural practices and can be a valuable tool for promoting physical, mental, and spiritual well-being.
Highlights of Mudra
Mudras are essential to many spiritual and cultural traditions and have been used for centuries to promote physical, emotional, and spiritual well-being. Here are a few reasons why mudras may be considered necessary:
- Mudras can be used as a tool for self-expression and communication. In Indian classical dances, for example, mudras are used to convey specific emotions or ideas through the movement of the hands.
- Mudras can be used as a tool for meditation and mindfulness. By focusing on the position and movement of the hands, a person can bring their attention inward and cultivate a sense of presence and awareness.
- Mudras can be used as a tool for self-healing and transformation. Many people believe that mudras have the power to evoke specific states of mind or to bring about physical, emotional, or spiritual benefits.
- Mudras can be used to connect with cultural and spiritual traditions. By practicing mudras, people may feel connected to their cultural or spiritual heritage and have a deeper understanding of their spiritual path.
Benefits Of Mudras
Mudras are believed to have various physical, emotional, and spiritual benefits. Some of the benefits that have been attributed to mudras include:
Physical Benefits
- Reducing stress and tension: Mudras help calm the mind and reduce feelings of stress and anxiety, which can positively impact the body.
- Improving circulation: Some mudras may help improve circulation and increase blood flow to different body parts.
- Promoting flexibility: Holding certain mudras for extended periods can help to improve flexibility in the fingers and wrists.
- Relieving pain: Mudras may help to relieve pain in the body, particularly in the head, neck, and shoulders.
- It’s important to note that while mudras may have some potential physical benefits, they must not be used as a substitute for medical treatment. If you are experiencing any physical discomfort or pain, you must consult a healthcare professional.
Emotional Benefits
- Reducing stress and anxiety: Mudras may help to calm the mind and reduces feelings of stress and anxiety.
- Improving mood: Mudras may help to improve mood and promote feelings of relaxation and well-being.
- Enhancing focus and concentration: By helping to quiet the mind, mudras may improve focus and concentration.
- Promoting feelings of inner peace: Mudras may help connect the individual with their inner self, leading to inner peace and tranquility.
Spiritual Benefits
- Promoting self-awareness: Mudras may help to bring the individual’s focus inward, allowing for a deeper exploration of the self.
- Enhancing spiritual practice: Mudras may enhance spiritual practice, such as meditation or yoga.
- Connecting with the divine: For some individuals, practicing mudras may help to facilitate a connection with the divine or a higher power.
- Promoting spiritual growth: By helping to quiet the mind and bring the individual’s focus inward, mudras may help to facilitate spiritual growth and self-discovery.
Course Curriculum Mudra Teacher Training
Introduction to Mudras
Learn the basics of Mudras, including its types, history, and benefits for the mind and body.
Science Behind Mudras Logical Understanding behind the principles of mudras, and practical exercises to feel the energy.
Section 1 – Fundamentals Of Hand Mudra
- Programme Overview
- Basics Of Mudras
- Basics Of Kundalini
- Basics Of Chakras
- Mudra Meditation
- Mudra in Daily Life
Section 2 – Basic Hand Mudras
- Vaayu Mudra – Mudra Of Air
- Buddhi Mudra – Mudra Of Mental Clarity
- Shunya Mudra – Mudra Of Emptiness
- Apana Mudra – Mudra Of Digestion
- Surya Mudra – Mudra Of The Sun
- Ruksha Mudra – Mudra Of Dryness
- Ushas Mudra – Mudra Of Dawn
- Akash Mudra – Mudra Of The Sky
- Prithvi Mudra – Mudra Of Earth
- Anjali Mudra – Mudra Of Prayer
Section 3 – Advanced Hand Mudras
- Root Chakra Mudra – Gyan Mudra
- Sacral Chakra Mudra – Shakti Mudra
- Solar Plexus Chakra Mudra – Rudra Mudra
- Heart Chakra Mudra – Lotus Mudra
- Throat Chakra Mudra – Granthita Mudra
- Third Eye Chakra Mudra – Kalesvara Mudra
- Crown Chakra Mudra – Mahamayuri Mudra
- Varun Mudra – Mudra Of Rain
- Apana Vayu Mudra – Mudra Of The Heart
- Dhyana Mudra – Mudra Of Meditation
- Linga Mudra – Mudra Of Heat
- Praana Mudra Of Life
- Hand Mudras For Major Common Ailments
Section 4 – Five Tattwas & Their Mudras
- Prithvi Tattva: Strengthening with Prithvi Mudra.
- Jala Tattva: Enhance life force with Prana Mudra.
- Agni Tattva: Ignite wisdom with Gyan Mudra.
- Vayu Tattva: Eliminate pain with Shoonya Vayu Mudra.
- Akash Tattva: Detox with Apana and Dhyan Mudra.
Section 5 – Hatha Yoga Mudra
Introduction
Mudras and prana
A scientific look at mudras
Five Groups of Yoga Mudras
-
- Hasta (hand mudras)
-
- Jnana mudra
-
- Chin mudra
-
- Bhairava mudra
-
- Hridaya mudra
-
- Chin Mudra while chanting ‘AAAA’
-
- Chinmaya Mudra while chanting ‘UUUU’
-
- Adi Mudra while chanting ‘MMMM’
-
- Brahma Mudra while chanting ‘AUM’
-
- Hasta (hand mudras)
-
- Mana (head mudras)
-
- Shambhavi mudra
-
- Nasikagra drishti
-
- Khechari mudra
-
- Shanmukhi mudra
-
- Mana (head mudras)
-
- Kaya (postural mudras)
-
- Vipareeta karani mudra
-
- Pashinee mudra
-
- Prana mudra
-
- Yoga mudra
-
- Manduki mudra
-
- Tadagi
-
- Kaya (postural mudras)
-
- Bandha (lock mudras)
-
- Maha mudra
-
- Maha bheda mudra
-
- Maha vedha mudra.
-
- Bandha (lock mudras)
-
- Adhara (perineal mudras)
-
- Ashwini mudra
-
- Adhara (perineal mudras)
Section 6 – Daily Health Mudra
a. Chin Mudra while chanting ‘AAAA’
b. Chinmaya Mudra while chanting ‘OU’
c. Adi Mudra while chanting ‘MMMM’
d. Brahma Mudra while chanting ‘AUM’
2.1. Mudras
Mudras and Chakras
1. Mooladhara Mudra (Root Chakra Gesture)
2. Swadhisthana Mudra (Sacral Chakra Gesture)
3. Manipura Mudra (Solar Plexus Chakra Gesture)
4. Anahata Mudra (Heart Chakra Gesture)
5. Hridaya Mudra (Compassionate Heart Gesture)
6. Vishuddha Mudra (Throat Chakra Gesture)
7. Ajna Mudra (Brow Chakra Gesture)
8. Vayu Mudra (Air Gesture)
9.Vyana Mudra (Expansive Prana Gesture)
11. Pranapana Mudra (Taking In and Throwing Out Gesture)
12. Udana Mudra (Upward Flying Energy Gesture)
13. Prana Mudra (Life Force Gesture)
14. Apana Mudra (Cleansing Energy Gesture)
15. Agni Mudra (Fire Gesture)
16. Linga Mudra (Mark of Siva)
17. Surya Mudra (Sun Seal)
18. Bhramara Mudra(Humming Bee Gesture)
19. Pushan Mudra (Giver of Good Health)
20. Kamajayi Mudra (Victory over Excessive Desires Gesture)
21. Shankha Mudra (Conch Shell Gesture)
22. Shunya Mudra(Silence of the Void Gesture)
23. Garuda Mudra (Eagle Gesture)
24. Kshepana Mudra (Letting Go Gesture)
25. Akasha Mudra (Touching the Void Gesture)
26. Shunya Mudra (Silence of the Void Gesture)
27. Bhu Mudra (Touching the Earth Gesture)
28. Kaleshwara Mudra (Lord of Time Gesture)
29. Prithivi Mudra (Earth Gesture)
30. Sukham Mudra (Stress Relief Gesture)
31. Vishnu Mudra (Universal Balance Gesture)
32. Varuna Mudra (Water-Balancing Gesture)
33. Jalodar Nashak Mudra (Water Reducing Gesture)
34. Mahatrika Mudra (Great Triangle Gesture)
35. Shakti Mudra (Essence of Power Gesture)
36. Ganesha Mudra (Remover of Obstacles)
37. Namaskar Mudra (My Essence Meets Your Essence Gesture)
38. Mandala Mudra (Circle Universe Gesture)
Pranayama Training
Yoga has become synonymous with term Asana; however the entire practice of Yoga is based on practices of consciousness. Asana, Pranayama, Mudra and Bandhas are the three most important techniques that lead to the state of higher level of meditation. When these four techniques are done with awareness, knowledge and preparation, Yoga becomes possible. In this journey to self-discovery, pranayama leads to the purification of senses, prana and mind. With a consolidated state of mind one attains Mudra and maintains bandhas in order to maintain one pointed awareness. Learn these four important practices in Yoga and let your practice be to attain the state of Yoga itself.
synonymous with term Asana; however the entire practice of Yoga is based on practices of consciousness. Asana, Pranayama, Mudra and Bandhas are the three most important techniques that lead to the state of higher level of meditation. When these four techniques are done with awareness, knowledge and preparation, Yoga becomes possible. In this journey to self-discovery, pranayama leads to the purification of senses, prana and mind. With a consolidated state of mind one attains Mudra and maintains bandhas in order to maintain one pointed awareness. Learn these four important practices in Yoga and let your practice be to attain the state of Yoga itself.
Yoga has become synonymous with the term Asana; however, the entire practice of Yoga is based on practices of consciousness. Asana, Pranayama, Mudra and Bandhas are the three most important techniques that lead to the state of a higher level of meditation. When these four techniques are done with awareness, knowledge, and preparation, Yoga becomes possible. In this journey to self-discovery, pranayama leads to the purification of senses, prana and mind. With a consolidated state of mind, one attains Mudra and maintains bandhas in order to maintain one-pointed awareness. Learn these four important practices in Yoga and let your practice be to attain the state of Yoga itself.
Pranayama
Pre-practices, practical hints, seasonal considerations, technical considerations, benefits and modifications of pranayama practices.
What you will learn from this course?
- Four aspects of pranayama
- Pranic body & five koshas (sheaths)
- The five types of prana
- Pranayama’s health benefits
- Pranayama in spiritual context
- The respiratory system
- Yogic breathing and different types of Pranayama
- Neurological and physiological benefits of pranayama
- Benefits of Pranayama
- Types of pranayama and levels
- How to Practice and teach pranayama
- Relevance of pranayama in modern life
- How to practice meditation correctly
- How to teach meditation
- How to develop the right voice & script
- How to setup and structure a class
- Evidence based benefits of meditation
- Meditation and neuroscience
- An overview of different meditation traditions
- Fundamental principles of meditation
- Understand the science behind meditation
- Understand the difference between different meditation styles
- Important do’s and don’t s of teaching meditation
- Anatomy for finding the right sitting position
- How to integrate meditation in daily life

Curriculum Pranayama Teacher Training
1.Techniques Training & Practices (TTP)
- What is Prana?
- Prana and Kundalini Shakti
- Naadis (Energy Channels)
- Chakras (Energy Centers)
- The Five Koshas (Sheaths)
- Subtle Bodies
- Essential Guidelines of Pranayama
- Sixteen Types of Pranayama
- Udar Pranayama (Abdominal Breathing)
- Vaksha Pranayama (Thoracic Breathing)
- Jatruka Pranayama (Clavicular/Collarbone Breathing)
- Yogic Pranayama
- Kapalbhati Pranayama (Skull Shining Breathing)
- Chandra Pranayama (Moon Breathing)
- Surya Pranayama (Sun Breathing)
- Chandrabhedi Pranayama (Moon-piercing Breathing)
- Suryabhedi Pranayama (Sun-piercing Breathing)
- Anulom Vilom Pranayama (Alternate nostril Breathing)
- Naadi Shodhana Pranayama (Energy channel cleansing Breathing)
- Bhastrika Pranayama (Bellow Breathing)
- Sitkari Pranayama (Hissing Breathing)
- Sheetali Pranayama (Cooling Breathing)
- Ujjayi Pranayama (Victorious Breathing)
- Bhramari Pranayama (Honey bee humming Breathing)
- Yoga Mantra Chanting
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Mantras
- Gayathri Mantra
- Maha Mrityunjaya Mantra
- Saha nāv avatu
- Sarve bhavantu sukhinaḥ
- 3. Health Benefits of Pranayama
- Physical Benefits
- Psychological Benefits
- Emotional Benefits
- Vital Benefits
- Spiritual Benefits
- Anatomy & Physiology of Respiratory system
Anatomy & Physiology of Pranayama
1.1. Gaseous Exchange:
1.2. Respiratory System
- a) Larynx:
- b) Trachea (wind pipe)
- c) Bronchi
- d) Bronchioles
- e) Alveoli (Air sacs)
1.3. Lungs
1.4. Pleura
- External Anatomy
1.5. Bronchi
- 6. Pulmonary Ventilation:
1.7. Respiration Mechanism
- a) Shallow breathing
- b) Deep Breathing
- c) Unconscious control of breathing
- d) Conscious control of breathing
1.8. Lung Volume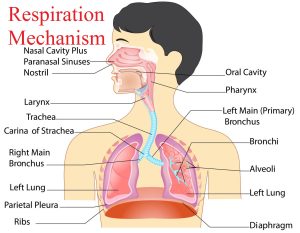
- Total air volume
- Tidal volume
- Vital capacity
- Philosophy of Pranayama
- History of Yoga
- Philosophy of Yoga
- Philosophy into Practice
- Ayurveda – Allied Practice of Yoga
- Contraindications, Misalignments, & Adaptations
- Relevance of Pranayama in modern life
- Learn the important guidelines for teaching Pranayama
- Introduction of Ashtanga Yoga
- First Limb – Yama
- Second Limb – Niyama
- Third Limb – Asana
- Fourth Limb – Pranayama
- Fifth Limb – Pratyahara
- Sixth Limb – Dharana
- Seventh Limb – Dhyana – Meditation
- Eighth – Samadhi – Super Consciousness
- 6. Teaching Methodology
- Sequencing
- Environment for Yoga
- Cueing
- Class Management
- How to Practice and teach Pranayama
- How to setup and structure a class
- Professional Development
- Ethical Commitment
- Yoga Professionalism Guidelines
- Practicum
- The Practicum (Teaching Practice)
- Mudra
5.1. Introduction
5.2. Mudras and prana
5.3. A scientific look at mudras
5.4. Mudras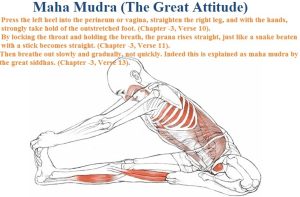
- Jnana mudra
- Chin mudra
- Bhairava mudra
- Hridaya mudra.
- Shambhavi mudra
- Nasikagra drishti
- Shanmukhi mudra
- Yoga mudra
- Bandhas (neuro-muscular locks)
6.1. Introduction to Bandha
6.2. Granthis
6.3. Bandha (lock)
- Jalandhara Bandha (throat lock)
- Moola Bandha (perineum contraction)
- Uddiyana Bandha (abdominal contraction)
- Maha Bandha (the great lock)
- Yoga Nidra
- Introduction
- Yoga Nidra steps
- Preparation/Introduction
- Relaxation
- Sankalpa/Resolve
- Rotation of Consciousness
- Breathe Awareness
- Feeling of Sensations
- Image visualization
- Sankalpa/Resolve
- Finish
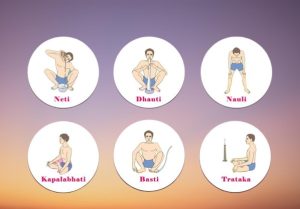
- Shatkarma (internal cleansing)
- Jala Neti (nasal cleansing with water)
14.Warm Up For pranayama
- Seated warm up
- Child’s Pose Balasana
- Tabletop Pose
- Cat and Cow Stretch
- Supine Twist Jathara Parivartanasa
- Thread the Needle Parsva Balasana
- Knees-to-Chest Apanasana
- Downward-Facing Dog
- Upward-Facing Dog Urdhva Mukha Shvanasana
- Hands in & out Breathing
- Hands stretch breathing
- Ankle stretch breathing
- Tiger breathing
- Dog breathing
- Rabbit breathing
- Alignments of Sitting Asanas (Poses)
- Vajrasana (Thunderbolt/ Adamantine/ Diamond Pose)
- Ardh Padmasana (Half Lotus Pose)
- Siddhasana(Psychic Pose)
- Padmasana (Lotus Pose)
How to Register?
Please Contact Us (karunaayoga@gmail.com or +91 9686549129)
